AI for RNA-Seq Embeddings in Transcriptomic Profiling
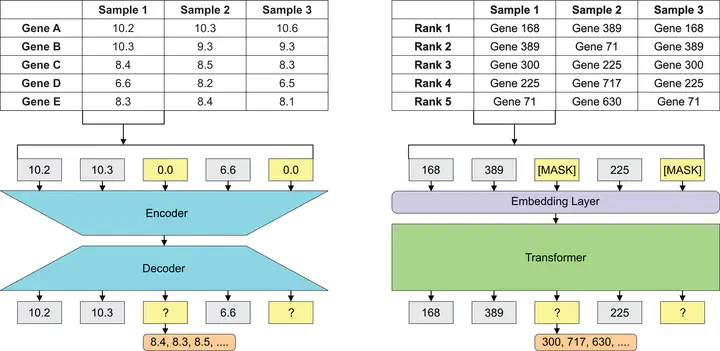
Gene embeddings leverage large RNA-seq datasets by capturing co-expression patterns, allowing deep neural networks (DNNs) to numerically characterize gene functions and regulatory roles. These models are highly sensitive to how RNA-sequencing data is encoded, which can vary from traditional, raw expression values to ranking-based approaches, as inspired by word embeddings in natural language processing. This project investigates how input representations and tokenization methods interact with various network architectures and their impact on biological inference.
Preliminary results show similar performance for cell line prediction, while raw embeddings outperform ranked embeddings in masked pretraining, with largest errors at mid-ranked genes. Ongoing work will evaluate additional downstream tasks and explore hybrid architectures to integrate both representations, aiming to capture complementary transcriptomic features and improve prediction accuracy across tasks.